An accessible website for every user
WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) are guidelines that have been drawn up for digital accessibility. A website should be usable by everyone. Even if you have a disability. Think of people who are deaf or visually impaired, people who cannot use a mouse or people with concentration problems. But don't forget the temporary restrictions either. You can break your arm or maybe you just had surgery on your eyes. This means you have to navigate through a website in a different way. With an accessibility review, we check whether your website is accessible to everyone.

Why would you want to make your website accessible?
Your reach will increase, because now everyone can visit your website.
Your website will be easier to find in the search engines, because it is easier to scan.
You increase the user-friendliness of your website, which increases the chance of a conversion.
It is a legal obligation for government institutions and municipalities to be completely barrier-free from 2019.

Ready for a second opinion?
Let's talk about how we can help you improving the accessibility of your website.
Improve accessibility in 5 steps
A complete accessibility review consists of 5 steps. For optimal results you'll have to go through all these steps. Depending on the result, you can also choose to have an accessibility statement drawn up (step 5) immediately after the report (step 2).
Step 1. Check current accessibility
We investigate whether your website is practically accessible with tools and devices that are also used by people with disabilities. For this we use our accessibility toolkit. Of course we also check whether the website meets the mandatory accessibility requirements according to the WCAG.
Step 2. Improvement report
We present our findings in a report. This contains quick wins that an experienced developer can quickly implement. We also make suggestions for structural solutions that require more long-term planning. You can contact us or another development party with this report.
Step 3. Implement improvements to your website
You have come to the right place with our development team to implement both the quick wins and the structural solutions. Sometimes the quick wins are not enough to take your website to the right level. This means more structural solutions are needed, or we have to take a side step in order to be able to move forward afterwards. Such a side step could be that we improve the performance of your website, or let an interaction designer help you think about the user interface of your product. Our project managers are happy to help and guide you on the improvement process.
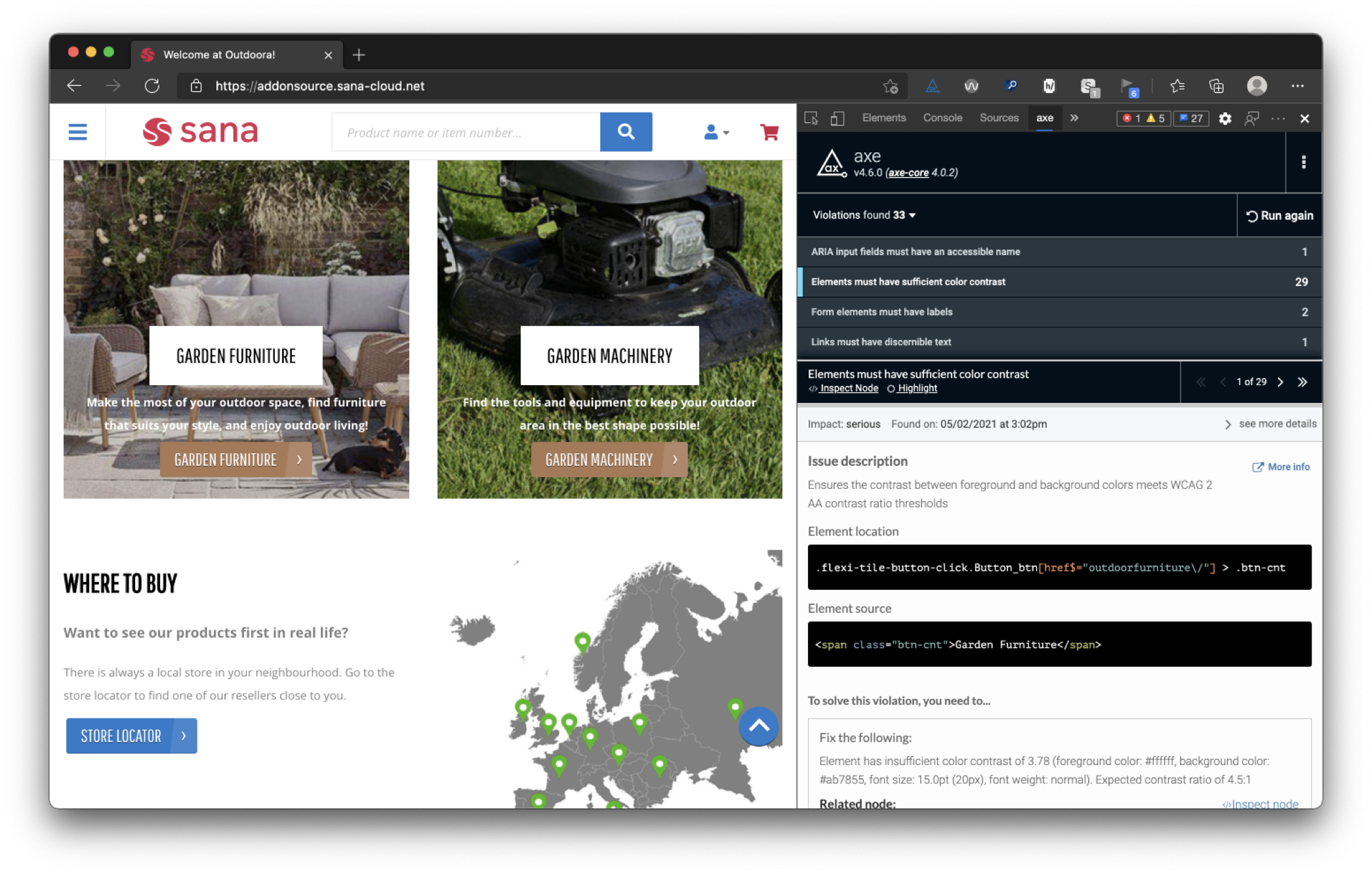
Step 4. Test and re-evaluate
After implementing the improvements, we test your website or app again for accessibility. The summary ensures that your score is higher and meets the digital accessibility requirements.
Step 5. Prepare and submit an accessibility statement
To demonstrate that your website has been checked for accessibility, you will receive an official accessibility statement from us. This document has been drawn up according to the model of the Dutch government, whereby your website is given a compliance status. The status indicates how accessible your app site is and what actions are ultimately planned to make your app site accessible. You can place the accessibility statement on your website and submit it to toegankelijkheidsverklaring.nl.

Fantastic to work with! Great quality output of our Accessibility Review with attention to detailWorkvivo
Why do an accessibility review at De Voorhoede?
Our developers have a lot of experience in building websites and making them accessible. We can therefore interpret the results well and convert them into technical solutions. That is tailor-made technology, tailored to the target group and the budget, because there is no panacea.
You can also do an accessibility study yourself. But checking your own website on the WCAG is a bit like a butcher inspecting his own meat.
There are various parties that can conduct an accessibility study for you. The advantage is that we can really improve the accessibility of your website or app. Not every research agency has the expertise to do this themselves.
European Accessibility Act 2025
The European Accessibility Act will come into force at the 28 of June 2025. This means that all European websites, both government and non-government, must be digitally accessible to everyone. Also for people with disabilities. The accessibility requirements will probably be simliar with the WCAG. Small businesses are likely to be exempted from certain obligations.
The details of the European accessibility law are still being worked out. It is clear that this law is coming. Therefore, be regularly updated and start making your website accessible.
Digital Accessibility Act
Legislation that regulates accessibility can be divided into two parts: legislation for (semi) government and legislation for companies. Since 1 July 2018, the 'Tijdelijk besluit digitale toegankelijkheid overheid' has been in effect. This stipulates that all government and semi-government websites and apps must be accessible to everyone. This also applies to intranets that go live or are substantially modified after this date. The decision is based on the EU directive on the accessibility of websites and mobile applications of public authorities, which has been in force since December 22, 2016.
Since 1 January 2017, the amended 'Wet gelijke behandeling op grond van handicap of chronische ziekte' (Wgbh/cz) also applies. This stipulates that websites of companies offering goods and services must be accessible to everyone. If a website is not accessible, the citizen can appeal to this law and ask for adjustments. If the citizen is not heard, he can go to the College voor de Rechten van de Mens.
In other words: accessible is the norm and if you want to deviate as a company, you need well-founded reasons for this. What constitutes a well-founded reason is vague. Adjustments are defined as "simple amenities". If improving accessibility is 'disproportionately burdensome', it is not necessary, for example if the adjustment costs a lot of time and money. As an example: Rabobank had to make the internet banking app accessible in 2017 after a complaint to the College voor de Rechten van de Mens.
Who does the legislation apply to?
The decree only applies to the (semi) government:
State, regional or local government agencies, for example national government, water boards and municipalities;Public-law institutions, including the Central Bureau of Statistics, the Dutch bank, Bureau Jeugdzorg and Staatsbosbeheer;
Partnerships of this.
The Equal Treatment Act applies to both (semi)government and companies.
Requirements for a website
The obligations of a government website to comply with the decision can be divided into two parts:
The website must be WCAG 2.1 Level A and AA compliant.
The website must have an accessibility statement.
Exceptions
Specific situations and exceptions apply. The guiding principle here is that everything should be made accessible as much as possible. An example: a painting with a low contrast does not need to be made accessible, because this affects the integrity of the artwork.

Do you have a question about our Accessibility Review?
We're all ears! Contact Jasper